Retrieving eggs in order to perform IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) consists of three steps. Learn more about the steps and how the eggs are retrieved in this article.
The ovaries are the organs in our body which contain our eggs. Our eggs develop in small fluid filled sacs called follicles which are contained within the ovary. In order to perform in vitro fertilization, eggs must first be collected from the ovary. This procedure is called egg retrieval, or ovum pickup. The use of vaginal ultrasound makes it possible to visualize the ovaries.
First step: Ultrasound
Before you can undergo IVF, you must first have an ultrasound to determine the position of the ovaries. Most egg retrievals are performed by a vaginal approach, but sometimes a transabdominal route is needed if the ovaries are located high in the pelvis. Sometimes uterine fibroids make reaching the ovaries more difficult. This step will ensure your doctor can safely and successfully collect eggs from your ovaries. This article will focus on transvaginal oocyte retrieval.
Second step: Fertility medication
For most patients, fertility medications will be administered to help multiple ovarian follicles develop. Ultrasound and blood tests will be performed to determine when the follicles are likely to contain eggs that are mature. This process is call ovarian stimulation. The egg retrieval procedure will be timed by the administration of medication to cause the eggs to mature. This is often called the “trigger shot”. This make the eggs capable of being fertilized by sperm.
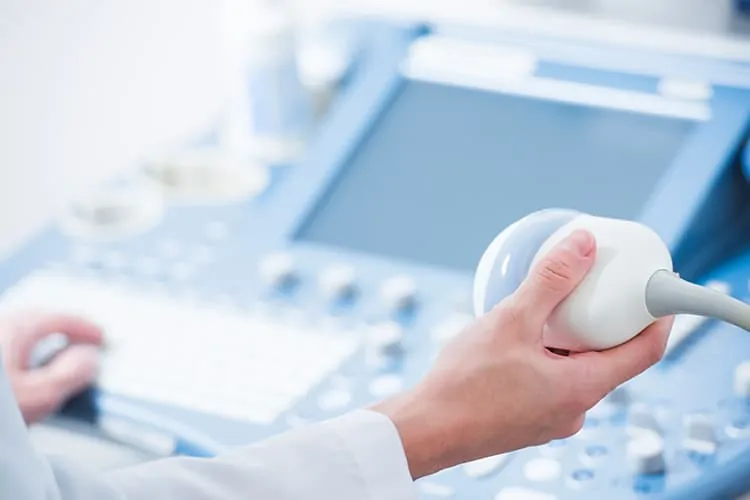

Third step: Egg retrieval
The egg retrieval procedure will be performed typically 36 hours after the trigger shot. Patients will usually be asked to fast after midnight before the procedure if anesthesia or sedation is planned. Upon arrival to the procedure area, you may have an intravenous line placed so that medications can be administered to help you feel relaxed and comfortable during the procedure. These medications are often administered by an anesthesiologist or other trained professional.
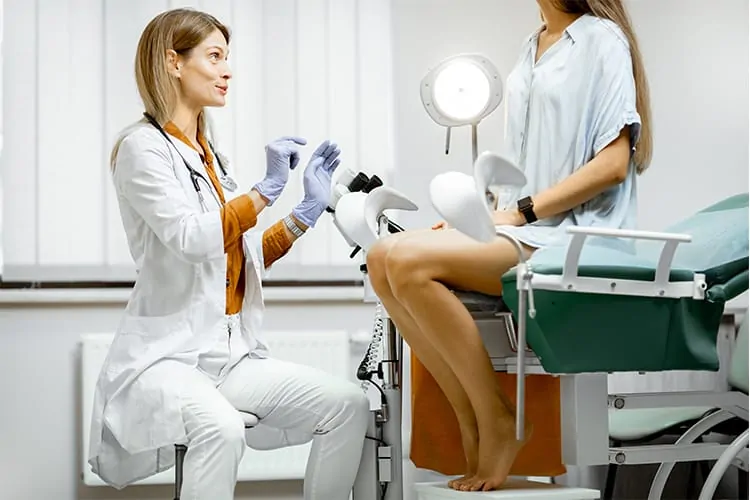
Once in the procedure room, you will be positioned for retrieval. This means lying on back with your legs or feet in stirrups, similar to a routine gynecological or Pap smear examination. Your vagina and external genital area (vulva) will be cleansed with saline or antiseptic solution.
A vaginal ultrasound probe with a special needle attached to it will be placed into the vagina. The doctor will be able to see your ovaries and carefully insert the needle through the vaginal wall into the ovary and into each follicle.
Suction will be used to drain the fluid out of each follicle. The eggs will be travel into the needle and collected into test tubes. These will be given to the embryologists who will identify the eggs and prepare them for fertilization or in some cases, freezing for fertility preservation. This same procedure is repeated for the second ovary. After all of the eggs are collected, the needle and vaginal probe are removed. A speculum is placed into the vagina to inspect the needle stick sites to check for bleeding. A sterile sponge is use to apply pressure to the site if needed.
After the procedure is complete, you will be awakened and brought to a recovery area, where you will be observed by a nurse. You may experience pelvic discomfort, and pain medicine can be administered if needed. You may experience some cramping and spotting afterwards
After the egg retrieval
The actual procedure usually takes 10-15 minutes. Typically, patients can go home within an hour of completing the procedure. You will not be able to drive that day but you can resume most normal activities the following day. Your doctor will provide you with specific postoperative instructions. You should contact your doctor’s office right away if you experience severe pain, feel lightheaded or dizzy, or experience fainting after the procedure, as this may be a sign of bleeding from the ovaries, which is rare.



